Understanding Tooth Erosion: Causes, Effects and Prevention
Introduction
Tooth erosion is a prevalent dental concern, marked by the gradual wearing down of tooth enamel. In this comprehensive blog post, we delve into the various causes that contribute to tooth erosion, shedding light on factors that significantly impact dental health. Understanding these elements is pivotal in effectively addressing and preventing tooth erosion. Let’s explore the key reasons behind tooth erosion and equip ourselves with the knowledge needed for a healthier, vibrant smile.
What causes tooth erosion?
- Acid foods and drinks:
Acidic substances such as citrus fruits, sodas, and vinegar-based dressings can erode tooth enamel over time. - Frequent consumption of sweet foods:
Bacteria in the mouth feed on sugars and produce acids that can lead to enamel erosion and tooth decay. - Gastrointestinal problems:
Conditions such as acid reflux and vomiting can bring stomach acids into the mouth, which can erode enamel. - Dry mouth (xerostomia):
Reduced saliva production can create a more acidic environment in the mouth, which contributes to enamel erosion. - Abrasive teeth cleaning:
Using a toothbrush with hard bristles or brushing too vigorously can cause enamel wear. - Bruxism (teeth grinding):
Constant grinding or clenching of the teeth can gradually erode the enamel.
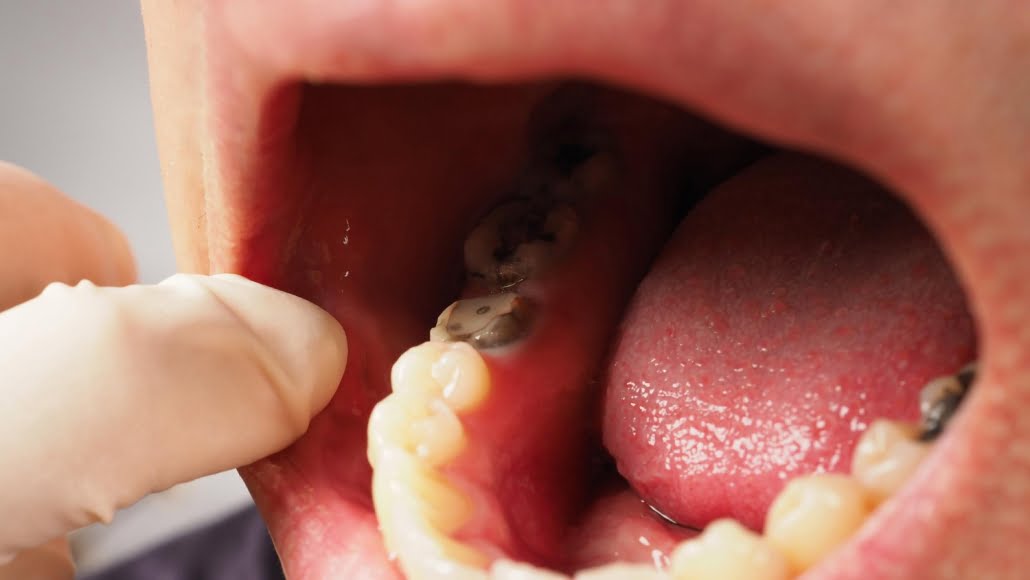
Effects of tooth erosion
- Teeth sensitivity:
Eroded enamel exposes dentin, leading to increased tooth sensitivity to hot, cold or sweet stimuli. - Colour Change:
Teeth may appear yellowish as the dentin becomes more visible due to enamel loss. - Rounded edges of teeth:
Eroded teeth may have rounded or sandblasted edges that change their appearance. - Cracks and chips in the teeth:
Weakened enamel is more prone to cracking or flaking. - Dental cavities:
Enamel erosion can create pockets or holes in the teeth, which encourages the development of cavities.
Prevention and management
- Balanced diet:
Eat a balanced diet with a minimum of acidic and sweet foods. Opt for tooth-friendly choices like dairy, nuts, vegetables and fruits. - Proper oral hygiene:
Brush your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and a soft-bristled toothbrush. Daily floss for cleaning the interdental spaces. - Regular dental check-ups:
See your dentist for regular checkups and cleanings to monitor your dental health and address issues quickly. - Drink water:
Drink plenty of water throughout the day to maintain a healthy pH in your mouth and help flush away acids and food debris. - Sugar Free Chewing Gums:
Chewing sugar-free gum stimulates the production of saliva, helps neutralize acids and protects tooth enamel. - Use a straw:
Use a straw when consuming acidic or sugary drinks to minimize direct contact with the teeth. - Wear a Night Watch:
If you grind your teeth at night, consider using a night guard to protect your enamel.
Conclusion
Tooth erosion is a serious dental problem that requires attention and proactive care. By understanding its causes and effects and taking preventative measures, you can preserve enamel and maintain good oral health. Regular dental examinations, a balanced diet, proper oral hygiene and careful eating habits are key components in preventing dental erosion and ensuring a healthy and bright smile.

Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!