Common Symptoms of Tooth Decay
Introduction:
A healthy smile is a reflection of overall well-being, and understanding the early indicators of tooth decay is paramount to maintaining optimal oral health. Tooth decay, a widespread oral health problem, can lead to discomfort, pain and more serious dental problems if left untreated. This comprehensive guide dives into the common symptoms of tooth decay and equips you with the knowledge needed to quickly identify these symptoms. From the subtlest of signs to more prominent concerns, we’ll explore the spectrum of symptoms that can serve as warning signs of potential tooth decay.
1. Tooth sensitivity:
One of the first signs of tooth decay is increased sensitivity to hot, cold, sweet or sour foods and drinks. Erosion of tooth enamel exposes the sensitive inner layers of the tooth, leading to discomfort when these stimuli come into contact with the affected tooth.
2. Toothache or pain:
As tooth decay progresses, the decayed area can spread deeper into the tooth and eventually reach the nerve endings. This can result in persistent toothache or sharp pain when biting or putting pressure on the affected tooth.
3. Bad breath (halitosis):
Tooth decay can contribute to bad breath due to the accumulation of bacteria and debris in the cavities or crevices of decayed teeth. If your breath constantly smells bad, tooth decay could be a potential cause.
4. Pus around the tooth:
Advanced tooth decay can lead to dental abscesses, which are pockets of pus that collect around the root of a tooth. The formation of pus often causes localized swelling, pain and an unpleasant taste in the mouth.
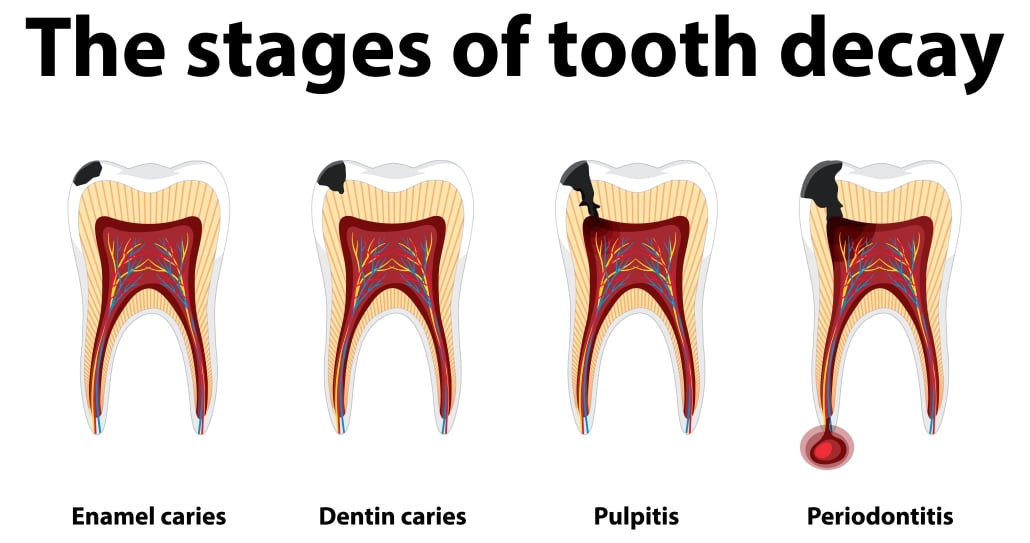
5. Visible holes or pits:
As decay progresses, it can form cavities or holes in the surface of the tooth. These hollows are not only unsightly, but also harbour bacteria that worsen the decay process.
6. Prolonged toothache from heat or cold:
If the discomfort from hot or cold substances persists even after the stimulus is removed, it could indicate that the nerve of the tooth has been affected by advanced decay.
7. Visible coloration:
Discoloration or visible stains on the surface of the tooth may indicate the presence of tooth decay. Stains can appear as white, brown or black spots that signal enamel erosion and the need for a quick dental examination.
8. Pain when chewing:
Tooth decay weakens the structural integrity of the tooth and makes it more susceptible to breaking or breaking, especially when subjected to the forces of chewing. Pain when chewing can be a sign of compromised dental health.
9. Shifting or loosening of teeth:
Because decay affects the supporting structures of the tooth, it can lead to displacement or loosening of the affected tooth. Changes in tooth alignment could indicate underlying decay-related problems.
10. Swollen or bleeding gums:
The decay can spread to the gums and cause irritation, inflammation and bleeding. If your gums appear red, swollen, or bleed easily, it is essential to consult a dentist for a thorough examination.
Conclusion:
Being vigilant in recognizing the signs of tooth decay allows individuals to take proactive measures to address potential dental problems. From tenderness and discoloration to pain and swelling, these indicators serve as valuable signals that require professional evaluation. Remember that routine dental check-ups and good oral hygiene practices are your allies in maintaining a healthy smile and preventing the progression of tooth decay.





Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!