Dental Plaque Prevention: Causes, Effects, and Effective Strategies
Introduction :
Dental Plaque Prevention is a common oral health problem that affects millions of people worldwide. It’s a sticky, colourless film of bacteria that forms on your teeth and can lead to a variety of dental problems if left untreated. In this comprehensive blog post, we’ll delve into the all-important Dental Plaque Prevention: what it is, how it forms, and most importantly, how you can get rid of it effectively. Understanding plaque is the first step to maintaining a healthy and beautiful smile.
Dental plaque: what it is, how it forms, and most importantly, how you can get rid of it effectively. Understanding plaque is the first step to maintaining a healthy and beautiful smile.
What is dental plaque?
Dental plaque is a biofilm that naturally forms on your teeth. It is a complex community of bacteria, saliva and food particles that adhere to the surface of the tooth. Although it starts out as a soft, almost invisible film, it can become thicker and harder over time, leading to a variety of oral health problems.
How is plaque formed?
Plaque formation is a continuous process that begins shortly after you brush your teeth. It usually develops like this:
Bacterial colonization: Your mouth is a bustling ecosystem that hosts countless bacteria. Some of these bacteria feed on the sugars and carbohydrates in the food you eat. When these sugars are digested, they produce acids as waste products.
Film formation: These acids, along with saliva and food particles, combine to form a thin sticky film on the teeth. This film is the initial stage of dental plaque.
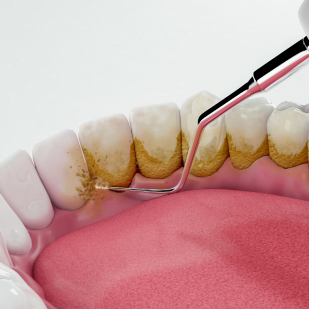
Aging: If this film is not removed, it begins to mature into dental plaque. Over time, minerals from your saliva become deposited in plaque, causing it to harden and become more difficult to remove. This hardened plaque is called tartar or calculus.
The danger of dental plaque
Plaque is not just an aesthetic problem; it is a serious threat to your oral health. Here are some of the problems that can arise from untreated plaque:
Cavities (cavities): Acids produced by plaque bacteria erode tooth enamel, leading to cavities or tooth decay. These cavities can be painful and may require fillings.
Gingivitis: Plaque buildup at the gum line can irritate and inflame the gums, causing gingivitis. Symptoms include redness, swelling and bleeding during brushing or flossing.
Periodontal disease: If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to a more serious condition known as periodontal disease (gum disease). This can lead to tooth loss and other serious health problems.
Bad breath (halitosis): Plaque can also contribute to persistent bad breath, as bacteria produce odorous byproducts.
Now that you know what dental plaque is and why it’s a problem, let’s explore how you can effectively get rid of it.
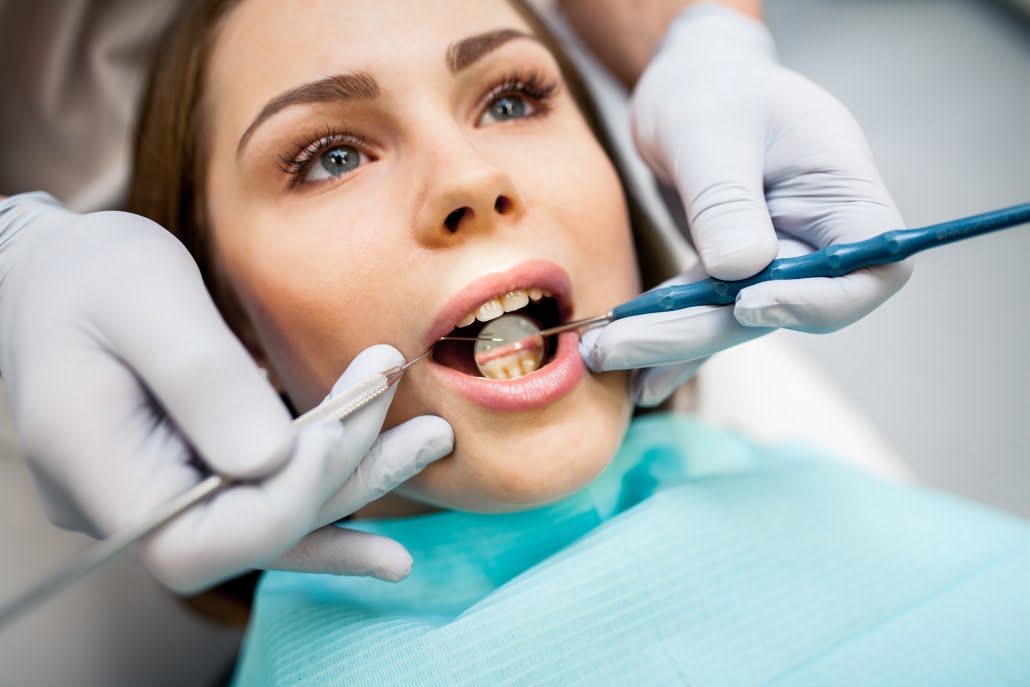
How to get rid of dental plaque
Brushing your teeth: Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste at least twice a day to brush your teeth. Brush for at least two minutes using gentle circular motions to cover all tooth surfaces.
Flossing: Daily flossing is essential to remove plaque and food particles from between the teeth and along the gum line.
Mouthwash: Consider using an antimicrobial or fluoride mouthwash as part of your daily oral care routine. It can help reduce plaque build-up and freshen your breath.
Correct brushing technique: Use a toothbrush with a small head to easily reach all areas of the mouth.
Brush gently but thoroughly, paying attention to the gum line and chewing surfaces of your teeth.
Replace the brush or brush head every 3-4 months or when the bristles show signs of wear.
Regular dental check-ups:See your dentist for regular checkups and professional cleanings. Your dentist can detect and remove any tartar build-up that you cannot remove at home.
Professional cleanings are usually recommended every six months, but your dentist may suggest a different schedule based on your individual needs.
Balanced diet and hydration:Limit sugar and starchy foods as they contribute to plaque formation. Instead, opt for a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean protein and whole grains.
Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help wash away food debris and bacteria.
Avoid smoking and tobacco products:Smoking and tobacco use can increase plaque build-up and lead to gum disease. Quitting smoking can greatly improve your oral health.
Consider dental products with anti-plaque properties:Some toothpastes and mouthwashes contain specific anti-plaque ingredients. Consult your dentist to find the right products for your needs.
Educate yourself and stay informed:Understanding the importance of plaque removal and its consequences is the first step to maintaining good oral health. Stay informed about the latest dental care techniques and products.
Conclusion
Dental plaque is a persistent adversary that can threaten your oral health. However, with proper oral hygiene practices, regular dental check-ups and a balanced diet, you can effectively manage and limit plaque build-up. By taking proactive steps to fight plaque, you will not only maintain a dazzling smile, but also promote overall oral health and prevent more serious dental problems. Remember, a little effort in plaque prevention today can save you from major dental problems tomorrow.





Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!